Changing screens/views/pages with ScreenManager - Kivy with Python Tutorials
In part 3 of this Kivy tutorial series, we're going to create a new page for our chat application. Once the user fills out the form for username, port, and ip, we want them to hit connect, and then connect to the server.
Code up to this point:
import kivy
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.label import Label
from kivy.uix.gridlayout import GridLayout
from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
# to use buttons:
from kivy.uix.button import Button
kivy.require("1.10.1")
class ConnectPage(GridLayout):
# runs on initialization
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.cols = 2 # used for our grid
with open("prev_details.txt","r") as f:
d = f.read().split(",")
prev_ip = d[0]
prev_port = d[1]
prev_username = d[2]
self.add_widget(Label(text='IP:')) # widget #1, top left
self.ip = TextInput(text=prev_ip, multiline=False) # defining self.ip...
self.add_widget(self.ip) # widget #2, top right
self.add_widget(Label(text='Port:'))
self.port = TextInput(text=prev_port, multiline=False)
self.add_widget(self.port)
self.add_widget(Label(text='Username:'))
self.username = TextInput(text=prev_username, multiline=False)
self.add_widget(self.username)
# add our button.
self.join = Button(text="Join")
self.join.bind(on_press=self.join_button)
self.add_widget(Label()) # just take up the spot.
self.add_widget(self.join)
def join_button(self, instance):
port = self.port.text
ip = self.ip.text
username = self.username.text
with open("prev_details.txt","w") as f:
f.write(f"{ip},{port},{username}")
print(f"Joining {ip}:{port} as {username}")
class EpicApp(App):
def build(self):
return ConnectPage()
if __name__ == "__main__":
EpicApp().run()
Now, we want to be able to change the pages/views/screens of our application. Up to this point, our EpicApp has just been:
class EpicApp(App):
def build(self):
return ConnectPage()
In order to change screens, we can use the ScreenManager from the Kivy Screen Manager.
from kivy.uix.screenmanager import ScreenManager, Screen
class EpicApp(App):
def build(self):
# We are going to use screen manager, so we can add multiple screens
# and switch between them
self.screen_manager = ScreenManager()
# Initial, connection screen (we use passed in name to activate screen)
# First create a page, then a new screen, add page to screen and screen to screen manager
self.connect_page = ConnectPage()
screen = Screen(name='Connect')
screen.add_widget(self.connect_page)
self.screen_manager.add_widget(screen)
# Info page
self.info_page = InfoPage()
screen = Screen(name='Info')
screen.add_widget(self.info_page)
self.screen_manager.add_widget(screen)
return self.screen_manager
Now that we've got that, we need to actually add our info page:
# Simple information/error page
class InfoPage(GridLayout):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
# Just one column
self.cols = 1
# And one label with bigger font and centered text
self.message = Label(halign="center", valign="middle", font_size=30)
# By default every widget returns it's side as [100, 100], it gets finally resized,
# but we have to listen for size change to get a new one
# more: https://github.com/kivy/kivy/issues/1044
self.message.bind(width=self.update_text_width)
# Add text widget to the layout
self.add_widget(self.message)
# Called with a message, to update message text in widget
def update_info(self, message):
self.message.text = message
# Called on label width update, so we can set text width properly - to 90% of label width
def update_text_width(self, *_):
self.message.text_size = (self.message.width * 0.9, None)
Now we modify the join_button method from ConnectPage
def join_button(self, instance):
port = self.port.text
ip = self.ip.text
username = self.username.text
with open("prev_details.txt","w") as f:
f.write(f"{ip},{port},{username}")
#print(f"Joining {ip}:{port} as {username}")
# Create info string, update InfoPage with a message and show it
info = f"Joining {ip}:{port} as {username}"
chat_app.info_page.update_info(info)
chat_app.screen_manager.current = 'Info'
Finally, change how we call our app:
if __name__ == "__main__":
chat_app = EpicApp()
chat_app.run()
The result:
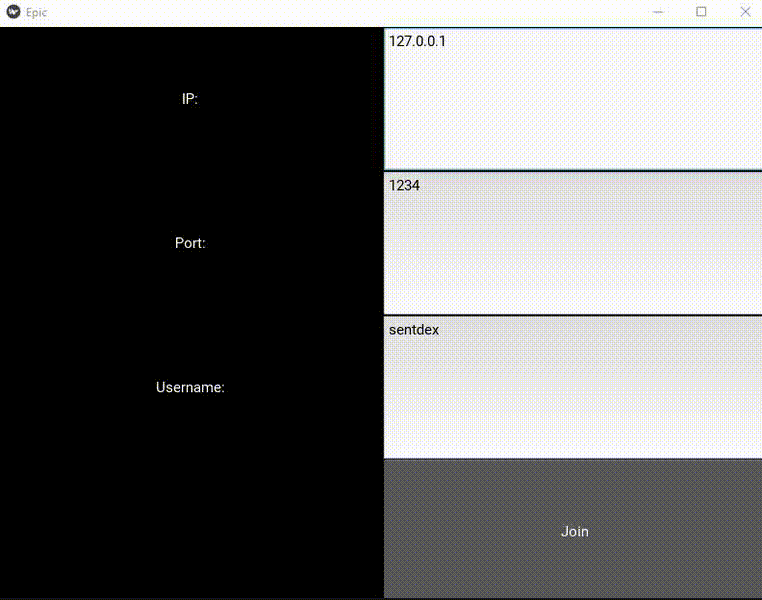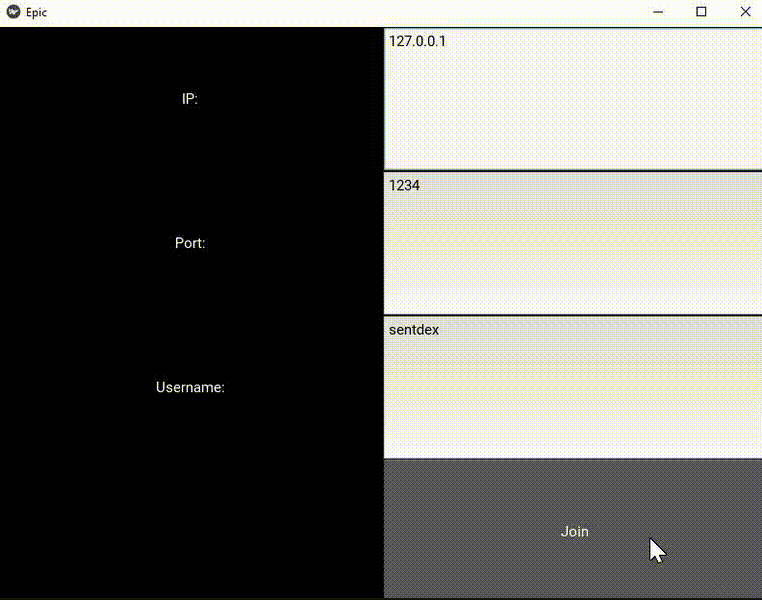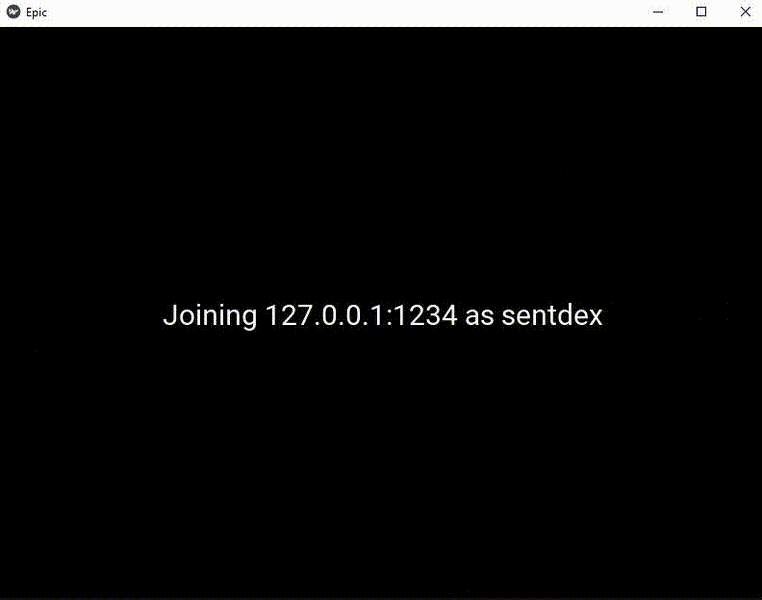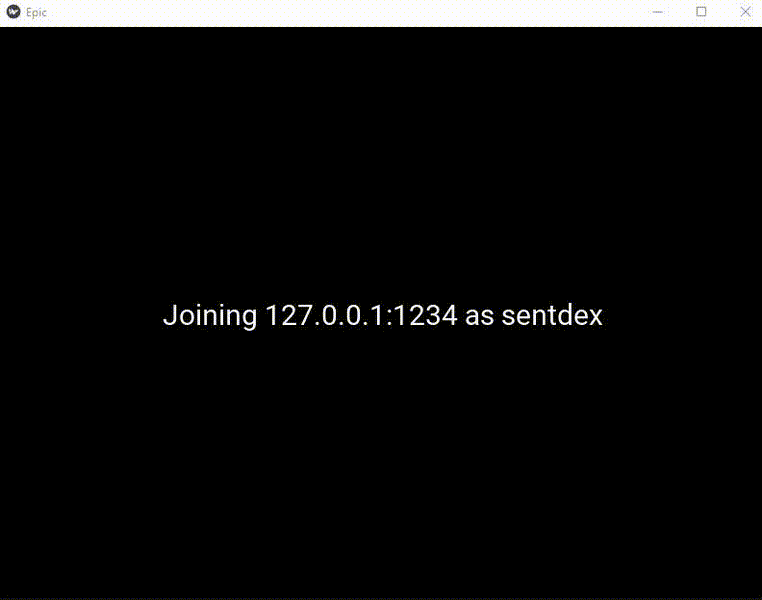
To connect, we're going to mainly be using our sockets chat app code. The files that we'll use for that:
socket_server.py
import socket
import select
HEADER_LENGTH = 10
IP = "127.0.0.1"
PORT = 1234
# Create a socket
# socket.AF_INET - address family, IPv4, some otehr possible are AF_INET6, AF_BLUETOOTH, AF_UNIX
# socket.SOCK_STREAM - TCP, conection-based, socket.SOCK_DGRAM - UDP, connectionless, datagrams, socket.SOCK_RAW - raw IP packets
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# SO_ - socket option
# SOL_ - socket option level
# Sets REUSEADDR (as a socket option) to 1 on socket
server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# Bind, so server informs operating system that it's going to use given IP and port
# For a server using 0.0.0.0 means to listen on all available interfaces, useful to connect locally to 127.0.0.1 and remotely to LAN interface IP
server_socket.bind((IP, PORT))
# This makes server listen to new connections
server_socket.listen()
# List of sockets for select.select()
sockets_list = [server_socket]
# List of connected clients - socket as a key, user header and name as data
clients = {}
print(f'Listening for connections on {IP}:{PORT}...')
# Handles message receiving
def receive_message(client_socket):
try:
# Receive our "header" containing message length, it's size is defined and constant
message_header = client_socket.recv(HEADER_LENGTH)
# If we received no data, client gracefully closed a connection, for example using socket.close() or socket.shutdown(socket.SHUT_RDWR)
if not len(message_header):
return False
# Convert header to int value
message_length = int(message_header.decode('utf-8').strip())
# Return an object of message header and message data
return {'header': message_header, 'data': client_socket.recv(message_length)}
except:
# If we are here, client closed connection violently, for example by pressing ctrl+c on his script
# or just lost his connection
# socket.close() also invokes socket.shutdown(socket.SHUT_RDWR) what sends information about closing the socket (shutdown read/write)
# and that's also a cause when we receive an empty message
return False
while True:
# Calls Unix select() system call or Windows select() WinSock call with three parameters:
# - rlist - sockets to be monitored for incoming data
# - wlist - sockets for data to be send to (checks if for example buffers are not full and socket is ready to send some data)
# - xlist - sockets to be monitored for exceptions (we want to monitor all sockets for errors, so we can use rlist)
# Returns lists:
# - reading - sockets we received some data on (that way we don't have to check sockets manually)
# - writing - sockets ready for data to be send thru them
# - errors - sockets with some exceptions
# This is a blocking call, code execution will "wait" here and "get" notified in case any action should be taken
read_sockets, _, exception_sockets = select.select(sockets_list, [], sockets_list)
# Iterate over notified sockets
for notified_socket in read_sockets:
# If notified socket is a server socket - new connection, accept it
if notified_socket == server_socket:
# Accept new connection
# That gives us new socket - client socket, connected to this given client only, it's unique for that client
# The other returned object is ip/port set
client_socket, client_address = server_socket.accept()
# Client should send his name right away, receive it
user = receive_message(client_socket)
# If False - client disconnected before he sent his name
if user is False:
continue
# Add accepted socket to select.select() list
sockets_list.append(client_socket)
# Also save username and username header
clients[client_socket] = user
print('Accepted new connection from {}:{}, username: {}'.format(*client_address, user['data'].decode('utf-8')))
# Else existing socket is sending a message
else:
# Receive message
message = receive_message(notified_socket)
# If False, client disconnected, cleanup
if message is False:
print('Closed connection from: {}'.format(clients[notified_socket]['data'].decode('utf-8')))
# Remove from list for socket.socket()
sockets_list.remove(notified_socket)
# Remove from our list of users
del clients[notified_socket]
continue
# Get user by notified socket, so we will know who sent the message
user = clients[notified_socket]
print(f'Received message from {user["data"].decode("utf-8")}: {message["data"].decode("utf-8")}')
# Iterate over connected clients and broadcast message
for client_socket in clients:
# But don't sent it to sender
if client_socket != notified_socket:
# Send user and message (both with their headers)
# We are reusing here message header sent by sender, and saved username header send by user when he connected
client_socket.send(user['header'] + user['data'] + message['header'] + message['data'])
# It's not really necessary to have this, but will handle some socket exceptions just in case
for notified_socket in exception_sockets:
# Remove from list for socket.socket()
sockets_list.remove(notified_socket)
# Remove from our list of users
del clients[notified_socket]
As well as
socket_client.py
import socket
import errno
from threading import Thread
HEADER_LENGTH = 10
client_socket = None
# Connects to the server
def connect(ip, port, my_username, error_callback):
global client_socket
# Create a socket
# socket.AF_INET - address family, IPv4, some otehr possible are AF_INET6, AF_BLUETOOTH, AF_UNIX
# socket.SOCK_STREAM - TCP, conection-based, socket.SOCK_DGRAM - UDP, connectionless, datagrams, socket.SOCK_RAW - raw IP packets
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
# Connect to a given ip and port
client_socket.connect((ip, port))
except Exception as e:
# Connection error
error_callback('Connection error: {}'.format(str(e)))
return False
# Prepare username and header and send them
# We need to encode username to bytes, then count number of bytes and prepare header of fixed size, that we encode to bytes as well
username = my_username.encode('utf-8')
username_header = f"{len(username):<{HEADER_LENGTH}}".encode('utf-8')
client_socket.send(username_header + username)
return True
# Sends a message to the server
def send(message):
# Encode message to bytes, prepare header and convert to bytes, like for username above, then send
message = message.encode('utf-8')
message_header = f"{len(message):<{HEADER_LENGTH}}".encode('utf-8')
client_socket.send(message_header + message)
# Starts listening function in a thread
# incoming_message_callback - callback to be called when new message arrives
# error_callback - callback to be called on error
def start_listening(incoming_message_callback, error_callback):
Thread(target=listen, args=(incoming_message_callback, error_callback), daemon=True).start()
# Listens for incomming messages
def listen(incoming_message_callback, error_callback):
while True:
try:
# Now we want to loop over received messages (there might be more than one) and print them
while True:
# Receive our "header" containing username length, it's size is defined and constant
username_header = client_socket.recv(HEADER_LENGTH)
# If we received no data, server gracefully closed a connection, for example using socket.close() or socket.shutdown(socket.SHUT_RDWR)
if not len(username_header):
error_callback('Connection closed by the server')
# Convert header to int value
username_length = int(username_header.decode('utf-8').strip())
# Receive and decode username
username = client_socket.recv(username_length).decode('utf-8')
# Now do the same for message (as we received username, we received whole message, there's no need to check if it has any length)
message_header = client_socket.recv(HEADER_LENGTH)
message_length = int(message_header.decode('utf-8').strip())
message = client_socket.recv(message_length).decode('utf-8')
# Print message
incoming_message_callback(username, message)
except Exception as e:
# Any other exception - something happened, exit
error_callback('Reading error: {}'.format(str(e)))
If you're interested in learning more about how the socket bits work here, check out the Python 3 sockets tutorial series. In our actual Kivy python code, we'll just do:
import socket_client
Okay great. In the next tutorial, we'll work on actually using the sockets, making the connection, and continuing to build out this chat application with Kivy!
-
Introduction to Kivy, a multi-platform GUI library for computers (Windows, Linux, Mac) and Mobile (iOS, Android) - Kivy with Python Tutorials
-
Buttons and Events - Kivy with Python Tutorials
-
Changing screens/views/pages with ScreenManager - Kivy with Python Tutorials
-
Scheduling tasks/functions/methods- Kivy with Python Tutorials
-
Chat Application Page - Kivy with Python Tutorials
-
Finishing Chat Application - Kivy with Python Tutorials
-
Packaging and Deployment (PyInstaller, Buildozer) - Kivy with Python Tutorials
